Leveraging Strategy, Metrics, and Agile Practices to Maximize Efficiency

How efficient is your organization?
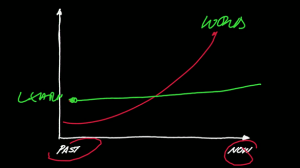
If you were to estimate how much of your team’s work actually translates into real, tangible outcomes, what would you say—60%? 70%? Most leaders assume that the majority of their team’s efforts drive meaningful results.
The reality, however, is far more alarming. Studies show that, on average, teams only accomplish 15% of work planned —the rest disappears into inefficiencies, misalignment, and hidden bottlenecks.
What if I told you that you could reclaim 10-20% or more of that lost capacity—not by working harder, but by identifying and addressing the key areas where work quietly drains away? By tackling these areas where process inefficiencies hide, organizations can dramatically increase their projected outcomes which means more delivery of services or products that customers can engage with and ultimately more money back to the company.
This white paper explores the seven critical leverage points that allow teams to recover lost work, reduce waste, and maximize productivity. Through a series of assessments and targeted workshops, Agile Accelerate is helping companies across the globe achieve more with existing resources using a targeted approach to find waste and attack it, leaving nothing on the table.
How Did This Happen?
In today’s complex and often isolated business structures, organizations often overestimate the efficiency of their operations. While many leaders believe that a significant portion of their team’s efforts directly contributes to organizational goals, the reality is starkly different. Research indicates that a substantial amount of work is lost due to various inefficiencies. McKinsey
A study by McKinsey & Company highlights that many organizations, despite adopting agile practices, are “ultimately doing so to deliver work and not value.” This misalignment between effort and value delivery underscores a critical issue in modern workplaces. McKinsey
The consequences of such inefficiencies are profound. Organizations face increased costs, delayed project timelines, and diminished employee morale. For instance, a report from the Project Management Institute found that for every $1 billion invested in projects, $122 million was wasted due to poor project performance. PMI.org
In many cases, engineering efforts are so splintered, that just the efforts to tackle technical debt is hindered by context switching to address code maintenance issues and operational tasks or non-coding issues.
Addressing these challenges presents a significant opportunity. By identifying and mitigating these inefficiencies, organizations can enhance productivity, reduce costs, and improve overall performance. Implementing targeted strategies to tackle these issues can lead to substantial gains in efficiency and value delivery.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into these inefficiencies, providing data-driven insights and practical solutions to help organizations reclaim lost productivity and achieve their strategic objectives.
Help!
If only 15% of work is truly delivering value, what happens to the rest? The answer lies in seven key areas—common but often overlooked pitfalls that drain capacity, create inefficiencies, and erode the impact of even the most well-intentioned teams. Understanding these areas is the first step toward reclaiming lost work.
- Dark Work – Tasks that consume time and resources but aren’t tracked or measured, making them invisible to leadership and impossible to optimize.
- Low-Value Stories – Work that gets done but contributes little to strategic goals, often due to unclear requirements or poor stakeholder alignment.
- Overhead – Administrative burdens, excessive meetings, reporting, and other non-value-adding activities that slow execution.
- Misalignment – When teams and leadership operate with different priorities, causing duplication, conflicting efforts, and wasted resources.
- DOWNTIME – Delays, handoffs, waiting for approvals, and other process inefficiencies that stretch timelines and reduce output.
- Poor Prioritization – Teams spread thin across too many initiatives, leading to context switching, burnout, and a lack of meaningful progress.
- Technical Debt – Short-term fixes and neglected system improvements that create long-term inefficiencies, making future work slower and costlier.
Each of these areas represents a recoverable loss—a place where small, targeted improvements can unlock 10-20% or more of lost capacity. By systematically addressing these issues, organizations can shift from merely working harder to working smarter, ensuring more of their effort translates into meaningful, high-value results.
What’s In It For Me?
At Agile Accelerate, we first work with organizations to assess what is currently being left on the table. A picture of this may be unique for different businesses, but many of the root causes are shared across industries.
Our company then crafts custom and targeted workshops that directly address the work loss challenges described above, along with their benefits and implications. In the past, we have offered services focused on giving the organization 100% control over the work committed to and delivered. Example workshops we have hosted include:
1. Facilitated Strategy Mapping
- Relevance to Work Loss: Many organizations struggle with inefficiencies because their teams lack clear alignment on objectives, critical success factors, and key activities. This leads to wasted effort on low-impact work.
- Benefits: This workshop helps teams refine their vision and create structured success factors, ensuring that efforts are focused on delivering actual value rather than just completing tasks.
- Implications: Companies that engage in strategic mapping can reduce misalignment, minimize duplicated efforts, and significantly improve the impact of their initiatives.
2. Metrics Audit and Strategy
- Relevance to Work Loss: Organizations often measure activity rather than value, leading to an overemphasis on busy work instead of meaningful outcomes.
- Benefits: By assessing gaps in current metrics and aligning them with value delivery, this workshop helps teams track progress in a way that drives impact rather than just motion.
- Implications: Businesses that refine their measurement strategies can better identify inefficiencies, eliminate unnecessary work, and redirect focus toward high-value outcomes.
3. Value Stream Mapping Workshop
- Relevance to Work Loss: Inefficiencies in workflow, handoffs, and bottlenecks often lead to excessive delays and wasted effort across teams.
- Benefits: This workshop enables organizations to visualize their end-to-end delivery process, pinpoint waste, and create actionable plans for improvement.
- Implications: By eliminating bottlenecks and streamlining workflows, organizations can enhance productivity, shorten cycle times, and improve overall efficiency.
4. Facilitated Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- Relevance to Work Loss: Many organizations implement surface-level fixes without addressing the systemic issues causing inefficiencies, leading to recurring problems.
- Benefits: RCA helps teams methodically analyze and identify the true sources of inefficiencies, ensuring solutions are impactful and long-lasting.
- Implications: Companies that perform root cause analysis can prevent repetitive failures, improve problem-solving capabilities, and reduce wasted time spent on rework.
These workshops provide concrete, actionable ways to tackle inefficiencies and reclaim lost productivity, ensuring that organizations are focusing on meaningful, value-driven work.
Act Now!
It’s time to leave nothing on the table and unlock your organization’s Full Potential.
The hidden inefficiencies in your organization—misaligned strategies, untracked metrics, fragmented collaboration, and unoptimized workflows—are costing you valuable time and resources. Agile Accelerate interactive workshops are designed to uncover and address these obstacles, empowering your teams to align on strategy, work smarter, and drive real, measurable impact.
Our sessions provide actionable insights and practical tools that help organizations streamline operations, enhance collaboration, and maximize value delivery. Whether you’re struggling with ineffective planning, lack of alignment, or missed opportunities for growth, our expert facilitators will guide you through targeted solutions that create lasting transformation.
The cost of inefficiency is too high to ignore. Let’s work together to reclaim lost capacity, strengthen your team’s agility, and ensure nothing is left on the table.
Contact Agile Accelerate today to explore how our workshops can drive immediate and lasting improvements in your organization.
Schedule a consultation now and take the first step toward transformational success!







 There are all sorts of ways to tell stories or build products—top-down, bottom-up, inside-out—each of which have their strong points. Sometimes it is most effective, for instance, to grab the user’s attention by initially giving them a nugget that might logically be placed in the middle of a narrative, and then providing necessary foundation, or by filling in the gaps as necessary. Could one apply the same process to learning from a book? I could imagine scanning through a book randomly, stopping at points that looked interesting and digesting a bit—much like I used to do with encyclopedias as a kid. Or, maybe, first reviewing the TOC for areas of interest, jumping to those sections, absorbing a bit, and then searching for any context that was missing. This would be a completely different way to learn from a book. I couldn’t call it reading, and don’t have a good term for it, other than a new kind of learning.
There are all sorts of ways to tell stories or build products—top-down, bottom-up, inside-out—each of which have their strong points. Sometimes it is most effective, for instance, to grab the user’s attention by initially giving them a nugget that might logically be placed in the middle of a narrative, and then providing necessary foundation, or by filling in the gaps as necessary. Could one apply the same process to learning from a book? I could imagine scanning through a book randomly, stopping at points that looked interesting and digesting a bit—much like I used to do with encyclopedias as a kid. Or, maybe, first reviewing the TOC for areas of interest, jumping to those sections, absorbing a bit, and then searching for any context that was missing. This would be a completely different way to learn from a book. I couldn’t call it reading, and don’t have a good term for it, other than a new kind of learning.